Abstract
Background: Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains a leading cause of global morbidity and mortality. With the increasing burden of CVD globally, there is a pressing need for innovative diagnostic and management solutions. The advent of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) offers promising avenues for addressing these challenges, with potential applications spanning from cardiac imaging to risk prediction.
Objective: This bibliometric analysis seeks to examine the scientific literature on AI and ML in cardiovascular disease.
Methods: A comprehensive bibliometric analysis was conducted on publications retrieved from PubMed, focusing on the role of AI and ML in CVD research from 2013 to 2023. The study zanalyzed publication growth rates, distribution by countries and journals, citations, funding sources, and keyword co-occurrence.
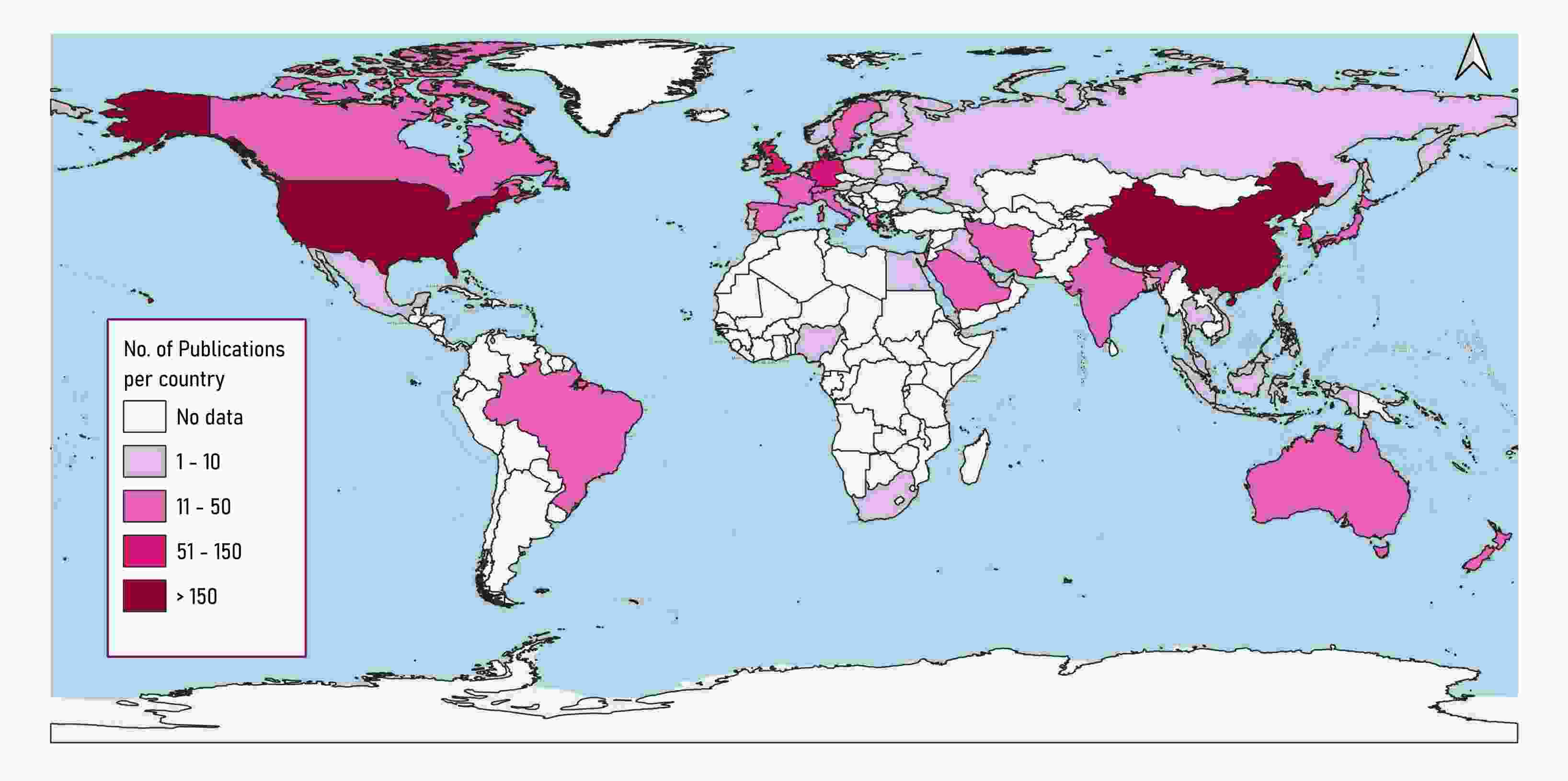
Results: A total of 895 articles were identified, showing an average annual growth rate of 32.6% in publications. The USA, China, and the UK emerged as leading contributors. The most cited article was "Artificial Intelligence in Precision Cardiovascular Medicine", with 394 citations. The National Institute of Health (NIH) was the top funding institution. Key recurring terms included "Machine learning," "Stroke", "Artificial Intelligence", and "Deep learning'.
Conclusions: Integrating AI and ML in cardiovascular medicine signifies a transformative shift, offering solutions to longstanding challenges in CVD diagnosis and management. The surge in publications over the past decade indicates growing interest and potential in this interdisciplinary field. However, as the technology continues to evolve, addressing its ethical and practical challenges is crucial.
Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence, ML, Cardiovascular Disease, Diagnosis and Management, VosViewer, Bibliometrics, CVD, Precision medicineReferences
Roth GA, Mensah GA, Johnson CO, et al. Global Burden of Cardiovascular Diseases and Risk Factors, 1990-2019: Update From the GBD 2019 Study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;76(25):2982-3021.
Kyu HH, Abate D, Abate KH, et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) for 359 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 195 countries and territories, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. The Lancet. 2018;392(10159):1859-1922.
Ruan Y, Guo Y, Zheng Y, et al. Cardiovascular disease (CVD) and associated risk factors among older adults in six low-and middle-income countries: results from SAGE Wave 1. BMC Public Health. 2018;18(1):778.
Yan Y, Zhang JW, Zang GY, Pu J. The primary use of artificial intelligence in cardiovascular diseases: what kind of potential role does artificial intelligence play in future medicine? J Geriatr Cardiol. 2019;16(8):585-591.
Secinaro S, Calandra D, Secinaro A, Muthurangu V, Biancone P. The role of artificial intelligence in healthcare: a structured literature review. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making. 2021;21(1):125.
Russak AJ, Chaudhry F, De Freitas JK, et al. Machine Learning in Cardiology—Ensuring Clinical Impact Lives Up to the Hype. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2020;25(5):379-390.
Karatzia L, Aung N, Aksentijevic D. Artificial intelligence in cardiology: Hope for the future and power for the present. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2022;9.
Huang J-D, Wang J, Ramsey E, Leavey G, Chico TJA, Condell J. Applying Artificial Intelligence to Wearable Sensor Data to Diagnose and Predict Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. Sensors. 2022;22(20):8002.
Romiti S, Vinciguerra M, Saade W, Anso Cortajarena I, Greco E. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Cardiovascular Diseases: An Unexpected Alliance. Cardiology Research and Practice. 2020;2020:4972346.
Pasrija P, Jha P, Upadhyaya P, Khan MS, Chopra M. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: A Paradigm Shift in Big Data-Driven Drug Design and Discovery. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(20):1692-1727.
Kilic A. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Cardiovascular Health Care. Ann Thorac Surg. 2020;109(5):1323-1329.
Lăcraru AE, Busnatu Ș S, Pană MA, et al. Assessing the Efficacy of a Virtual Assistant in the Remote Cardiac Rehabilitation of Heart Failure and Ischemic Heart Disease Patients: Case-Control Study of Romanian Adult Patients. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023;20(5).
Gouda P, Ganni E, Chung P, et al. Feasibility of Incorporating Voice Technology and Virtual Assistants in Cardiovascular Care and Clinical Trials. Current Cardiovascular Risk Reports. 2021;15(8):13.
Krittanawong C, Zhang H, Wang Z, Aydar M, Kitai T. Artificial Intelligence in Precision Cardiovascular Medicine. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2017;69(21):2657-2664.
van Eck N, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523-538.
Davenport T, Kalakota R. The potential for artificial intelligence in healthcare. Future Healthc J. 2019;6(2):94-98.
Tran BX, Latkin CA, Vu GT, et al. The Current Research Landscape of the Application of Artificial Intelligence in Managing Cerebrovascular and Heart Diseases: A Bibliometric and Content Analysis. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019;16(15).
Hu H, Wang D, Deng S. Global Collaboration in Artificial Intelligence: Bibliometrics and Network Analysis from 1985 to 2019. Journal of Data and Information Science. 3920;5(4):86-115.
Carriço G. The EU and artificial intelligence: A human-centred perspective. European View. 2018;17(1):29-36.
Mollura DJ, Culp MP, Pollack E, et al. Artificial Intelligence in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Innovating Global Health Radiology. Radiology. 2020;297(3):513-520.
Jiang F, Jiang Y, Zhi H, et al. Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke and Vascular Neurology. 2017;2(4):230-243.
Naik N, Hameed BMZ, Shetty DK, et al. Legal and Ethical Consideration in Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare: Who Takes Responsibility? Frontiers in Surgery. 2022;9.
Amisha, Malik P, Pathania M, Rathaur VK. Overview of artificial intelligence in medicine. J Family Med Prim Care. 2019;8(7):2328-2331.
Mahajan A, Vaidya T, Gupta A, Rane S, Gupta S. Artificial intelligence in healthcare in developing nations: The beginning of a transformative journey. Cancer Research, Statistics, and Treatment. 2019;2(2):182-189.
How to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 The Evidence

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright© by the author(s). Published by the Evidence Journals. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Pawan Kumar, Ahmad Neyazi, Roy Rillera Marzo, Celso Augusto Guimaraes, Joshuan J Barboza, Hashem Abu Serhan, Adnan Kisa, Sarath Lekamwasam, Vasso Apostolopoulos , Alfonso J. Rodríguez-Morales, Ranjit Sah, Mycoplasma pneumoniae returns: understanding its spread and growing impact , The Evidence: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2024): JAN - MAR
- Pawan Kumar, Vinay Suresh, Praveen Bharath Saravanan, Amit Kumar, Ayush Sharma, Battling bovine leukaemia virus: Unravelling the zoonotic transmission - a one health perspective , The Evidence: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2024): JAN - MAR