Abstract
Objective
The rapid deployment of COVID-19 mRNA vaccines, specifically Pfizer (BNT162b2) and Moderna (mRNA-1273), had raised concerns about rare cardiac side effects, notably myocarditis. The aim of this systematic review and meta-analysis was to comprehensively compare the risk of myocarditis associated with two mRNA COVID-19 vaccines: Pfizer (BNT162b2) and Moderna (mRNA-1273).
Methods
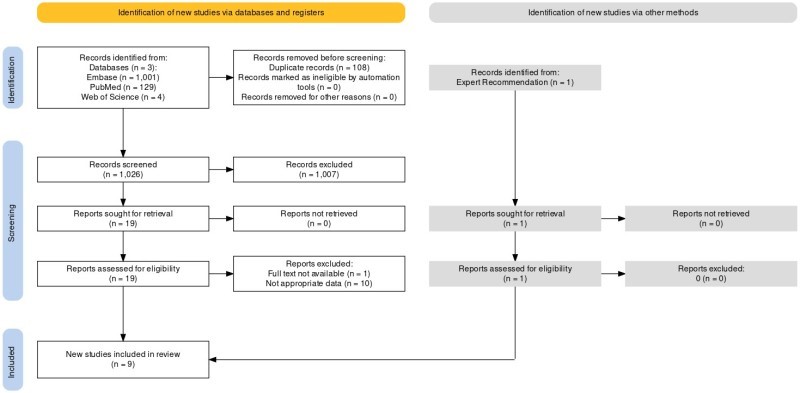
Following PRISMA guidelines, this review included observational cohort studies and case series comparing myocarditis risk in individuals receiving either of the two vaccines Pfizer (BNT162b2) and Moderna (mRNA-1273). Studies were identified through a systematic search of PubMed, EMBASE, and Web of Science. Data extraction focused on myocarditis incidence, demographic characteristics, vaccine type, and the number of doses. Meta-analysis was performed using a random-effects model. The risk of bias was assessed using JBI critical appraisal tools.
Results
Nine studies were found to meet the inclusion criteria, consisting of four cohort studies and five case series. Together, they encompassed data on 294,731,021 doses of the Moderna vaccine and 426,526,128 doses of the Pfizer vaccine. The combined risk ratio (RR) for myocarditis was 1.62 (95% CI: 1.02, 2.56) when comparing Moderna to Pfizer, suggesting a marginally increased risk with the Moderna vaccine, though it was not statistically significant. Additionally, a subgroup analysis based on the first and second doses indicated different risk levels. For the first dose, the RR was 1.14 (95% CI: 0.79, 1.64) for myocarditis in those who received Moderna compared to Pfizer. For the second dose, a higher RR of 1.69 (95% CI: 0.79, 3.59) was noted for myocarditis among Moderna recipients compared to Pfizer.
Conclusion
Myocarditis following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination was rare, with a very slight increased risk observed in Moderna recipients compared to Pfizer. These findings suggested the need for ongoing surveillance and further research to understand the nuanced differences in risk profiles between these vaccines.
Keywords:
mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, myocarditis risk, cardiac side effects, post-vaccination side effects, vaccine safetyHow to Cite
License
Copyright (c) 2023 Vijay Kumar, Mehak Dutt, Manya Soni

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Copyright© by the author(s). Published by the Evidence Journals. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited.
Most read articles by the same author(s)
- Manya Soni, DM Shilpa, Mirza Adil Beig, Exploring secure pathways: finding the most reliable malaria prophylaxis strategies for pregnant women with HIV , The Evidence: Vol. 2 No. 1 (2024): JAN - MAR